What Are Burndown Charts and Why Your Projects Need Them
Discover how burndown charts improve project management by visualizing progress, tracking team performance, and optimizing task management efficiency.
What Is a Burndown Chart?
A burndown chart is a simple visual tool that shows how much work is left in a project and how much time remains to complete it.
It’s mainly used in Agile project management, especially by teams working in short time periods called sprints. The chart displays time on the horizontal axis and remaining work on the vertical axis. As tasks are completed, the line moves downward. The goal is to reach zero remaining work by the end of the sprint or project.
Unlike tools such as Gantt charts that focus on task order and milestones, a burndown chart focuses on how fast work is being completed. This makes it easy for teams to see progress at a glance, spot delays early, and adjust their plans to stay on track.
Key Components of a Burndown Chart
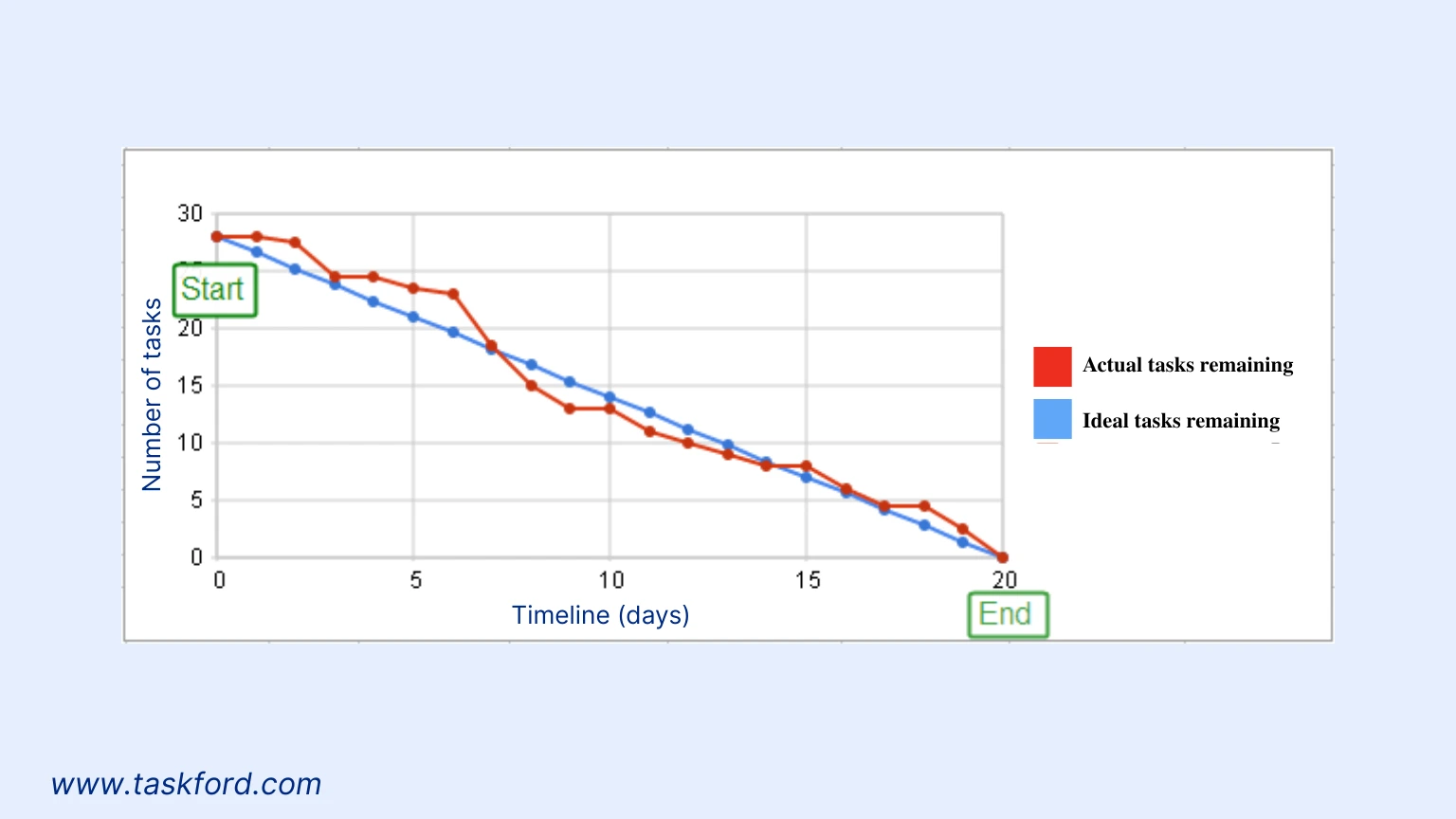
To understand how burndown charts function, let’s break down their core elements:
- X-Axis (Time): Shows the project timeline. This can be days, weeks, or sprints. It starts at the beginning of the project and ends at the deadline.
- Y-Axis (Work Remaining): Shows how much work is left. This is usually measured in tasks, story points, or hours. Story points represent the effort or complexity of the work.
- Ideal Work Line: A straight line that goes downward. It shows how work should be completed if everything goes as planned.
- Actual Work Line: Shows the team’s real progress. It is updated regularly and moves up or down based on how fast tasks are completed. Comparing it to the ideal line helps spot delays or faster progress early.
These components work together to provide a clear picture of project health, making burndown charts a powerful tool for task management and progress monitoring.
Types of Burndown Charts
Burndown charts are versatile and can be adapted to various project management needs. Here are the primary types and their applications:
- Sprint Burndown Chart: Tracks progress within a single sprint, typically lasting 1–4 weeks. It’s ideal for teams working on short, iterative cycles, helping them monitor daily task completion and adjust priorities to meet sprint goals.
- Release Burndown Chart: Focuses on a product release spanning multiple sprints, tracking progress toward delivering a set of features or requirements. This chart provides a high-level view of progress across sprints.
- Product Burndown Chart: Also called an epic burndown chart, this type tracks the overall progress of a product or large body of work. It’s useful for long-term projects, offering a strategic perspective on task completion.
- Budget Burndown Chart: Tracks financial expenditure against time, ensuring projects stay within budget. This type is particularly valuable for cost-conscious project management. Integrate with earned value management (EVM) practices to ensure financial control.
Each type serves a specific purpose, allowing teams to tailor their use of burndown charts to the scope and complexity of their projects.
Why Use Burndown Charts in Project Management?
Burndown charts offer numerous benefits for project management, making them a go-to tool for Agile teams. Here’s why they’re essential:
Real-Time Progress Visualization
Burndown charts clearly show how much work is left at any point in time. When teams update tasks regularly, they can track progress in real time and stay aligned. This visibility also supports transparency and accountability. For example, a team working on a two-week sprint to build a new website feature can use a burndown chart to check if they are on track to meet the deadline.
Early Identification of Bottlenecks
One of the main benefits of a burndown chart is that it shows the gap between planned progress and actual progress. If the actual work line stays above the ideal line, it means the team is falling behind schedule. This early signal helps project managers spot bottlenecks like limited resources or underestimated tasks and take action, such as shifting workloads or adjusting priorities.
Enhanced Team Collaboration
Burndown charts act as a shared reference that keeps everyone aligned. Teams can review the chart during daily stand-up meetings to discuss progress, identify challenges, and plan next steps. This transparency improves communication, keeps everyone focused on shared goals, and helps maintain team morale.
Improved Forecasting and Planning
By reviewing past burndown charts, teams can improve how they estimate work. For example, if tasks are often more complex than expected, the actual progress line will fall behind the ideal line. Tracking team velocity, which shows how quickly work is completed, helps teams create more accurate burndown charts for future sprints and plan their work more effectively.
Managing Scope Creep
Scope creep, where additional tasks are added mid-project, can derail timelines. Burndown charts make scope creep visible as spikes in the actual work line. By documenting and tracking new tasks, teams can discuss scope changes with stakeholders and adjust plans to maintain project alignment.
Limitations of Burndown Charts
Despite their advantages, burndown charts have limitations that teams should consider:
- Dependence on Accurate Estimates: Burndown charts rely on good task estimates. If story points or time estimates are off, the chart can give a misleading picture of progress. Teams can improve this by reviewing past sprints and adjusting estimates over time.
- No Task Priority Insight: The chart shows how much work is completed, but not which tasks are most important. High-priority and low-priority tasks look the same. Using burndown charts alongside prioritization tools helps teams focus on critical work first.
- Limited Scope Flexibility: Burndown charts assume a fixed amount of work. When new tasks are added, the chart can become harder to read. Burnup charts handle scope changes better, so using both can give a clearer overall view.
- No Quality Measurement: Burndown charts track completed tasks, not work quality. A task may be finished but still need fixes. Adding quality checks ensures completed work meets the required standards.
How to Create a Burndown Chart
Creating a burndown chart is straightforward with the right tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Define Tasks: List all tasks or user stories for the sprint or project. Assign story points or estimated hours based on complexity and effort.
- Set the Timeline: Determine the duration of the sprint or project (e.g., 10 days or 4 weeks).
- Establish the Ideal Line: Using historical data or team velocity, plot a straight line from the total work to zero by the deadline.
- Track Progress Daily: Update task statuses daily to plot the actual work remaining line.
- Analyze and Adjust: Review the chart during stand-ups or sprint reviews. If the actual line deviates from the ideal line, address issues by reallocating resources or reprioritizing tasks.
Most project management software automates this process, generating real-time burndown charts based on task updates.
Burndown Chart vs. Burnup Chart: What’s the Difference?
While burndown charts focus on remaining work, burnup charts track completed work, rising from zero as tasks are finished. Both are valuable in Agile project management:
- Burndown Charts: These charts plot how much work is left as tasks are finished. The line moves downward toward zero, making it easy to see if the team is on pace to meet a fixed deadline. They’re best for short sprints where the scope stays consistent.
- Burnup Charts: Burnup charts show how much work has been completed, rising upward as progress is made. They often include a total work line, helping teams visualize scope changes like new features added mid-sprint and their impact on delivery.
Teams can use both charts to gain a comprehensive view of project progress, switching based on project needs.
Best Practices for Using Burndown Charts
To maximize the value of burndown charts, follow these best practices:
- Update Regularly: Ensure task statuses are updated daily to keep the chart accurate.
- Refine Estimates: Use historical data to improve story point estimates for future sprints.
- Combine with Other Tools: Pair burndown charts with Kanban boards or prioritization tools to manage tasks effectively.
- Communicate with Stakeholders: Share charts during sprint reviews or client meetings to set clear expectations.
- Address Deviations Promptly: Act quickly if the actual work line trends above the ideal line, adjusting resources or priorities as needed.
Real-World Example: Burndown Charts in Action
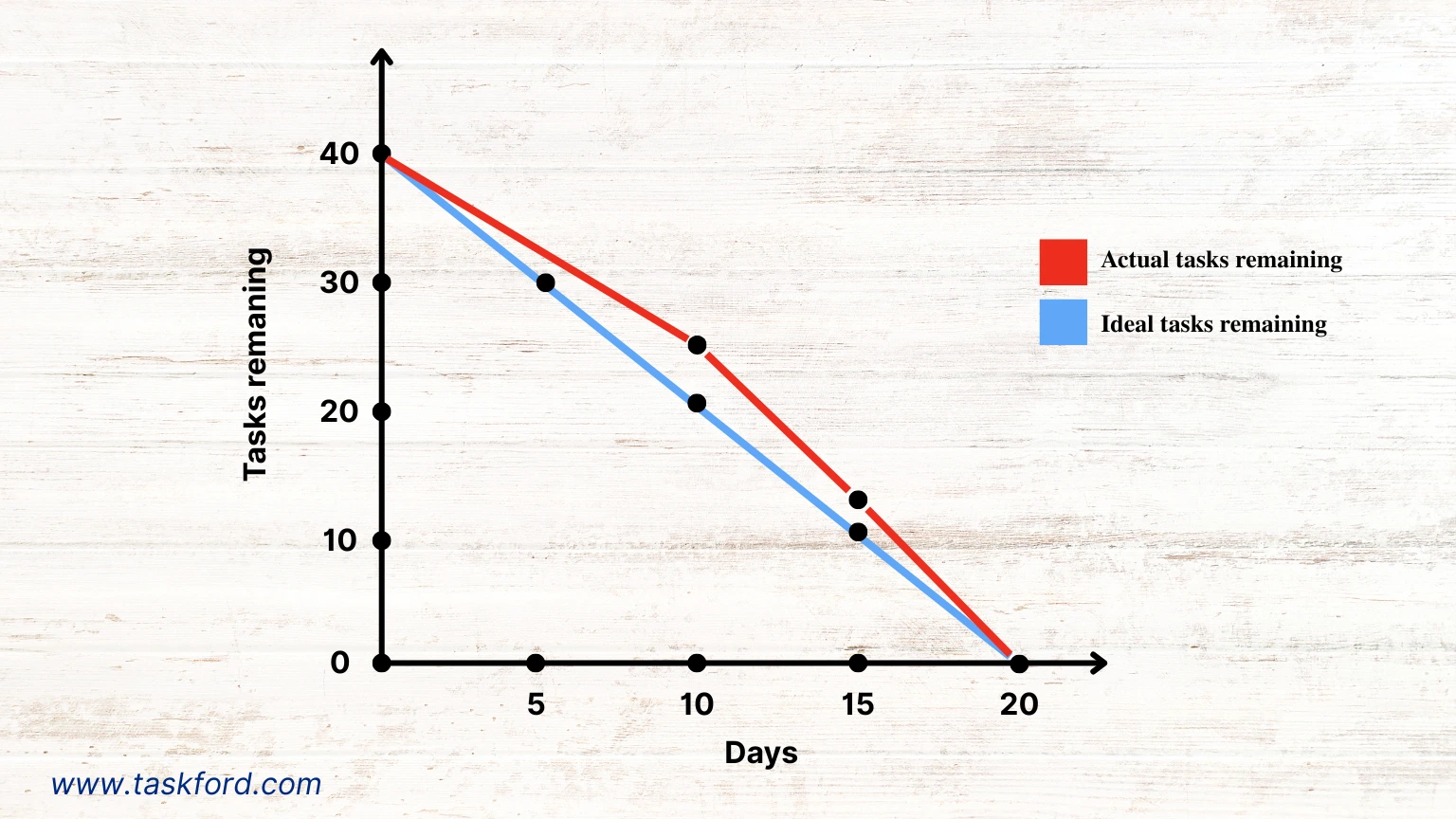
Imagine a team developing an e-commerce website over a four-week sprint with 40 story points of work, including tasks like designing the homepage, integrating payment gateways, and testing user flows. They create a sprint burndown chart with:
- X-Axis: 20 working days.
- Y-Axis: 40 story points.
- Ideal Line: A straight line from 40 story points on day 1 to 0 on day 20.
By day 10, the team has completed 15 story points, but the actual work line is above the ideal line, indicating slower progress. Analytics reveal that testing tasks are taking longer than estimated. The team reallocates resources to testing and adjusts priorities, bringing the actual line closer to the ideal line by day 15. By the sprint’s end, the project is completed on time, thanks to the burndown chart’s insights.
Using Burndown Charts with TaskFord
TaskFord simplifies how teams create and use burndown charts as part of everyday work delivery. With real-time execution tracking, automated reporting, and customizable dashboards, TaskFord helps teams generate accurate burndown charts for sprints, releases, or entire products based on live delivery data.
Key capabilities include:
- Work Delivery Management: Define work, assign story points, and update execution status. Burndown charts are populated automatically from real progress.
- Real-Time Delivery Updates: Charts reflect the latest execution as team members complete work, ensuring shared visibility at all times.
- Analytics and Velocity Insights: Use historical delivery data to refine estimates and understand team velocity for more confident planning.
- Team Alignment Tools: Share burndown charts during stand-ups or stakeholder meetings to keep teams aligned and accountable.
By combining burndown charts with TaskFord, teams gain clearer visibility into delivery progress, remove execution bottlenecks early, and deliver work on time with confidence and discipline.
Elevate Your Project Management with Burndown Charts
Burndown charts are a practical tool for tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and keeping teams focused on delivery. By clearly showing how much work remains, they help teams stay on schedule, manage scope changes, and plan more accurately. Whether you are working on a short sprint or a larger product release, burndown charts bring clarity and shared visibility to execution.
When used with TaskFord, burndown charts become part of a disciplined work delivery process. Teams can connect planning to execution, stay aligned around priorities, and achieve predictable, on-time delivery with greater confidence.
Learn more
- Agile Project Management - The Basics For Beginners
- Agile Project Management Sprint Cycle - From Planning to Retrospective
- Gantt Chart 101 - Definition, Key Features, and How to Use It for Project Management
Subscribe for Expert Tips
Unlock expert insights and stay ahead with TaskFord. Sign up now to receive valuable tips, strategies, and updates directly in your inbox.